In industrial automation and daily systems, electrical switches manage circuit flow, ensuring safety and efficiency. Understanding key electrical switch types helps businesses pick the right solutions. Here’s a breakdown of essential ones.
1. Manual Operation Electrical Switches: Reliable Hands-On Control
These require physical interaction, valued for simplicity and direct control.
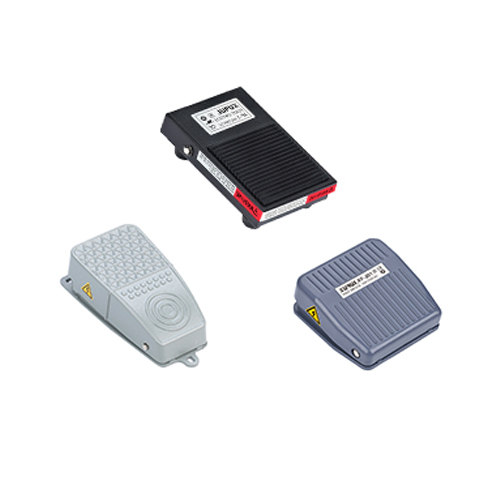
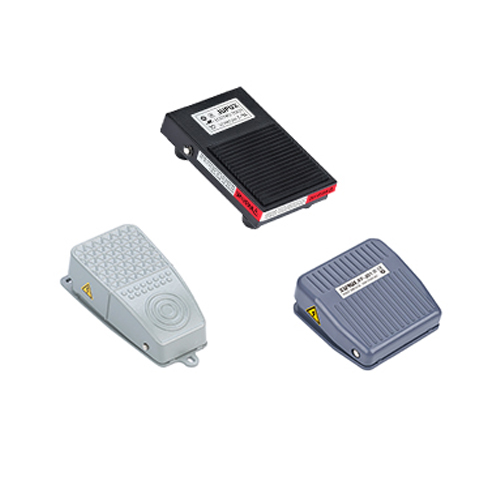
Foot Switches: Practical for Hands-Free Use
•Definition: An electrical switch activated by foot pressure, keeping hands free.
•Applications: Medical equipment, welding machines, assembly lines.
•Advantages: Boosts efficiency; durable pedal design handles frequent use.

Toggle Switches: Classic & Intuitive
•Definition: Electrical switches with a flipping lever for on/off, showing clear state.
•Applications: Household appliances, car dashboards, control panels.
•Advantages: Easy to maintain, cost-effective, good for simple adjustments.
2. Precision-Engineered Electrical Switches: For Sensitive Needs
Designed for minimal stimuli or position control, critical for accuracy and safety.
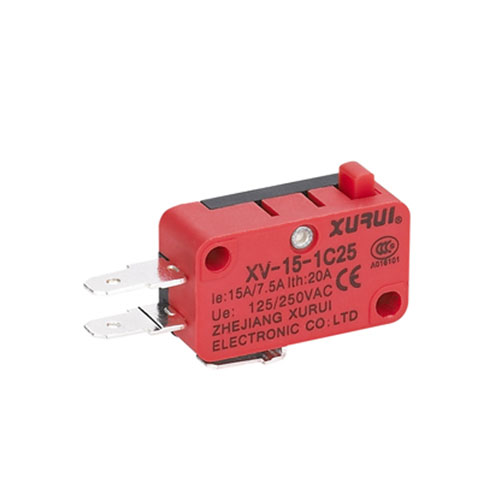
Micro Switches: Sensitive to Small Movements
•Definition: An electrical switch activating with tiny force (a few grams) via internal springs.
•Applications: Appliance sensors (e.g., fridge doors), industrial safety mechanisms.
•Advantages: Compact for tight spaces; quick response ensures reliability.
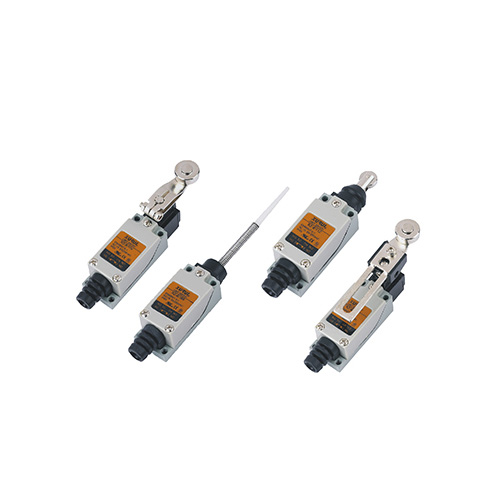
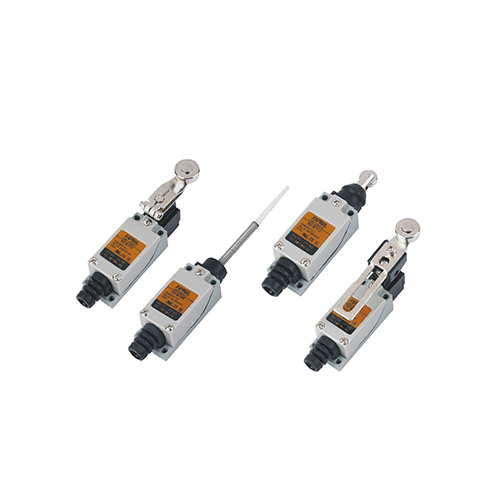
Limit Switches: Control Travel Safely
•Definition: Electrical switches stopping/starting mechanisms at preset positions to prevent overtravel.
•Applications: Conveyors, elevators, robotic arms, machine tools.
•Advantages: Protects machinery; ensures controlled movement in automation.

3. Sensor-Based Electrical Switches: Non-Contact Efficiency
Sensor-driven, no physical contact, offering durability in harsh environments.
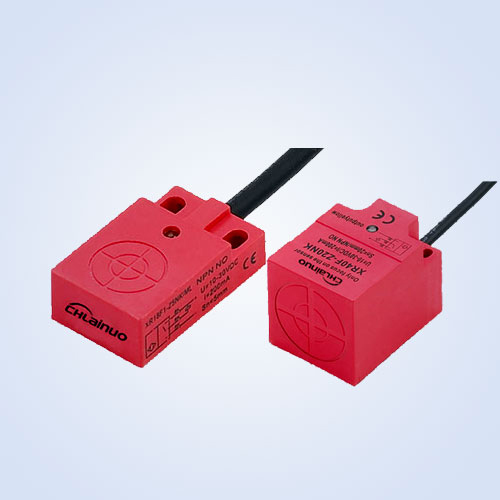
Proximity Switches: Non-Contact Detection
•Definition: An electrical switch detecting objects via electromagnetic/capacitive sensing, no touch.
•Applications: Manufacturing (counting, metal detection, component monitoring).
•Advantages: Works in dusty/wet conditions; less wear than mechanical switches.
Photoelectric Switches: Light-Driven Control
•Definition: Electrical switches using light beams (infrared/visible) to detect objects via beam interruption/reflection.
•Applications: Packaging, security, liquid monitoring, bottling machines.
•Advantages: Senses from a distance; suits high-speed operations, reduces stress.
Conclusion
From manual to precision and sensor-based, each electrical switch type fits specific needs. Choose based on operation mode, environment, and precision. They’re vital for efficient electrical control.Need the right electrical switch? Contact us for tailored advice.